How does canine distemper virus work
Canine distemper virus (CDV) poses a significant threat to canine health, disrupting critical bodily functions. By knowing how CDV operates, we can better protect our pets from its harmful effects.
CDV operates by binding its surface proteins to host cell receptors, initiating infection and spreading through the body, primarily affecting the respiratory, lymphatic, and nervous systems. Find more about the canine distemper virus.
How does canine distemper virus enter host cells?
CDV’s entry into host cells marks the beginning of a troubling invasion that leads to widespread infection. Understanding this process is crucial for developing preventative measures.
CDV enters host cells by binding its surface glycoproteins to cell receptors, allowing viral fusion and infiltration. This enables the virus to start the replication process, leading to systemic infection.

After getting inside the cells, CDV uses the host’s machinery for replication. As it multiplies, it starts spreading through the body. Prioritizing understanding of viral entry is key for developing inhibitors and vaccines.
Looking at viral mechanisms, CDV has surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin (H) and fusion (F) proteins that facilitate attachment and fusion with host cell membranes. Binding to SLAM (signaling lymphocyte activation molecule) on lymphocytes and nectin-4 on epithelial cells facilitates entry, influencing pathogenesis and clinical outcomes.
Which systems in the dog’s body are primarily targeted by CDV?
The impact of CDV on dogs isn’t limited to one system, making its effects more challenging to manage. Pinpointing target systems provides insights into treatment strategies.
CDV targets the respiratory, lymphatic, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems, leading to respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms, neurological issues, and weakened immunity.
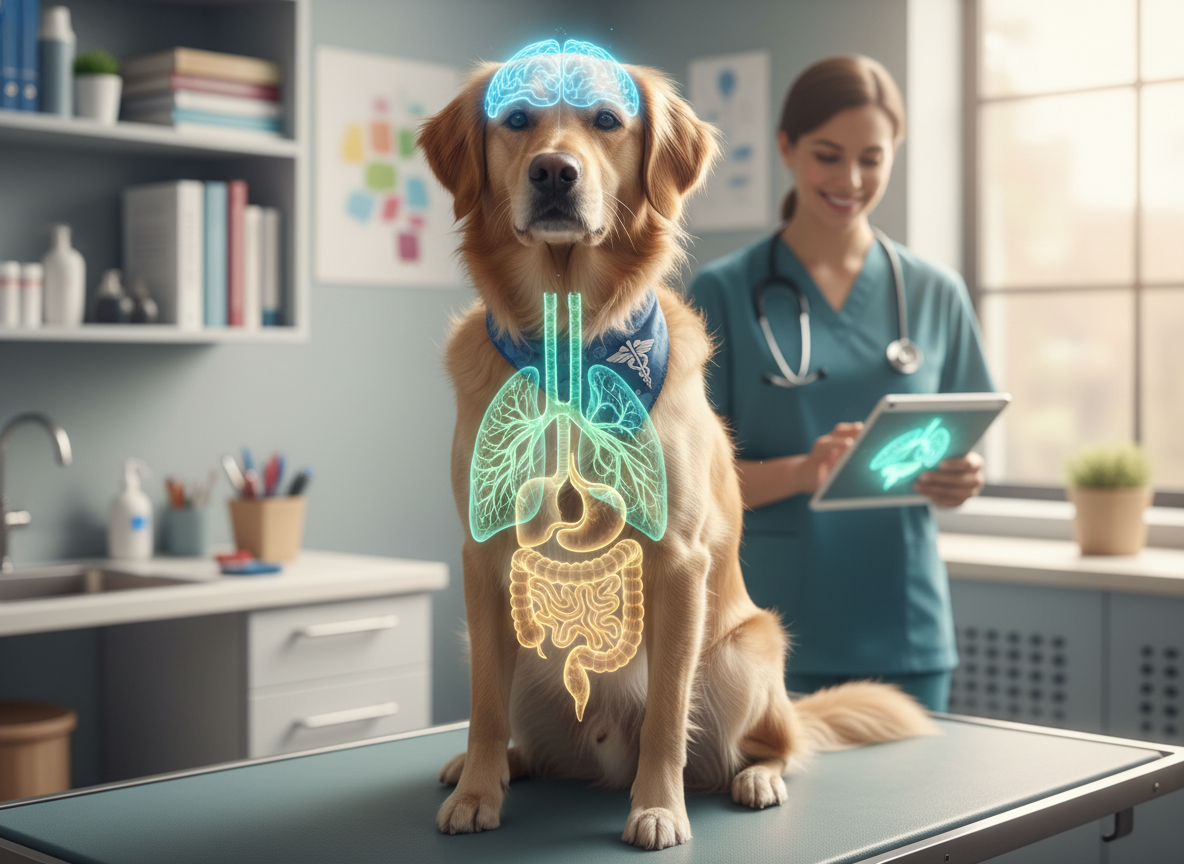

Recognizing affected systems aids in comprehensive disease management and symptomatic treatment. CDV’s interference with these systems requires multifaceted therapeutic approaches.
The virus first attacks the lymphatic system, debilitating the immune response. Progressing, it affects the respiratory system, causing pneumonia, the gastrointestinal system leading to diarrhea and vomiting, and eventually reaches the nervous system, causing encephalitis and seizures.
How does CDV affect the immune function of dogs?
CDV undermines a dog’s immune defenses, making the animal susceptible to other illnesses, necessitating protective measures. This understanding is vital for safeguarding canine health.
CDV compromises immune function by targeting lymphocytes, leading to immunosuppression. This makes dogs more vulnerable to secondary infections, exacerbating illness.
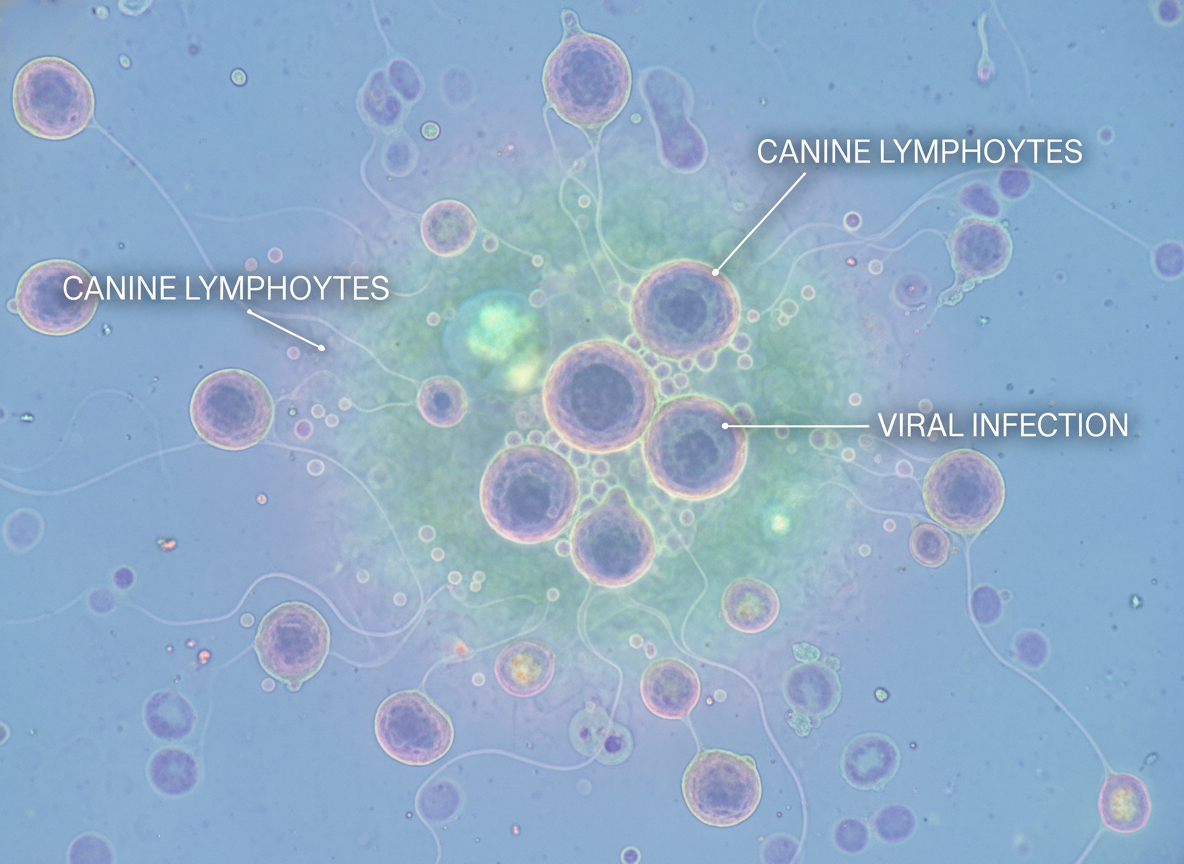
Preventing immunosuppression plays a central role in disease management. Rebuilding immune strength post-infection is essential for recovery and preventing complications.
CDV’s target on lymphocytes, specifically CD4+ and CD8+ cells, diminishes their population and function, thereby reducing the capability of the immune system to counteract pathogens. The reduction in T and B cell activity allows for opportunistic infections and worsened disease outcomes.
Why is understanding how CDV works important for disease control?
Grasping the complexities of CDV is essential for the effective control of the disease, which demands widespread efforts. With this knowledge, tackling CDV becomes manageable.
Understanding CDV’s workings aids in devising vaccines and treatments, reducing prevalence and improving animal health outcomes. Effective control hinges on viral mechanism comprehension. For more information, please contact cdv cpv ccv gia test suppliers.

Enhanced knowledge facilitates the creation of novel therapeutics and vaccines, targeting different viral stages and pathways. Broader immunization efforts benefit better disease management and control.
Mapping CDV’s genetic and structural characteristics allows for precision in intervention strategy, enabling preemptive and reactive measures. Vaccines targeting H and F proteins and receptor-blocking agents prove effective in halting disease progression, contributing significantly to disease control efforts. As a Veterinary Diagnosis Equipment Manufacturer, we are committed to providing the best solutions for disease control.
Conclusion
Understanding canine distemper virus mechanisms fosters smarter prevention and better treatment, securing pets’ health and long-term well-being.
References
- Canine Distemper – American Veterinary Medical Association
- Canine Distemper – Center for Food Security and Public Health
- Canine Distemper Overview – Merck Veterinary Manual



