Beschreibung
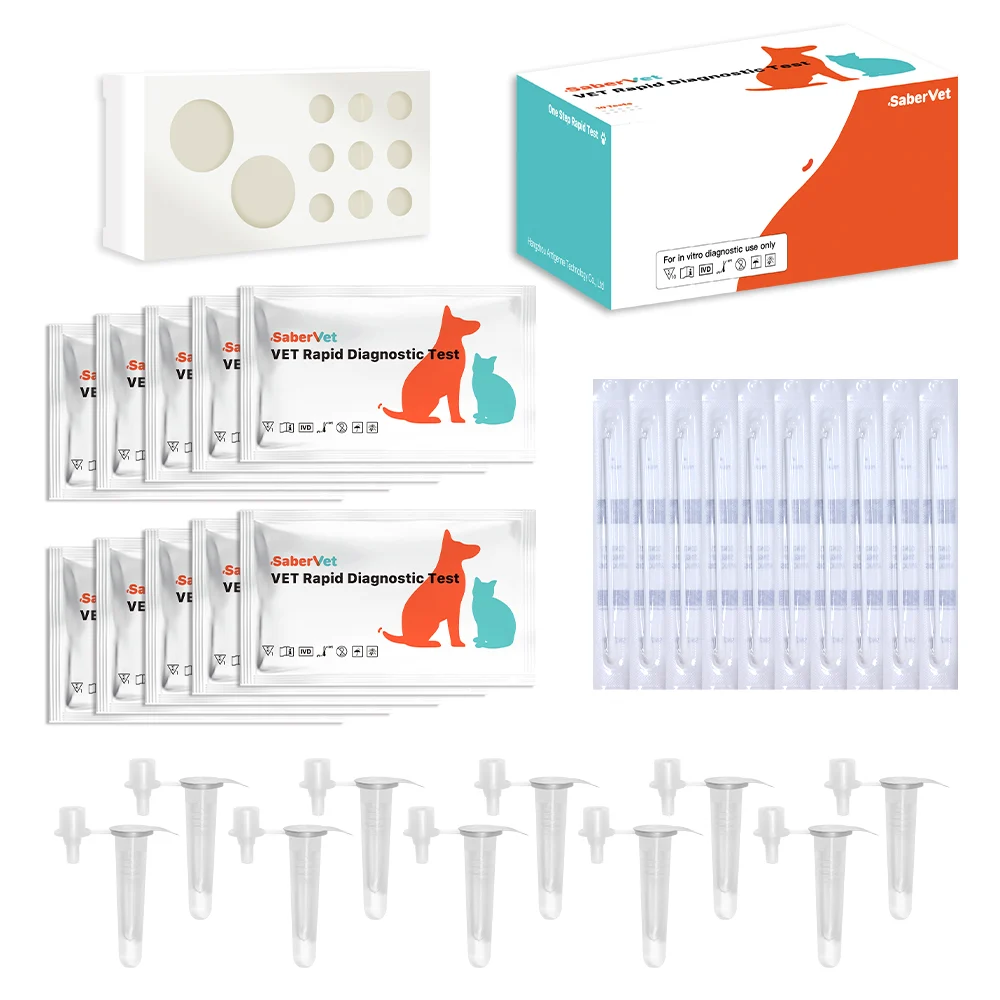
Inhalt
| Komponente | 10T/Karton |
| Testgerät | 10 Stück |
| Abstrich | 10 Stück |
| Puffer | 10 Stück |
Spezifikationen
| Name des Produkts | SaberVet Rabies Antigen Rapid Test |
| Markenname | Sabervet |
| Modellnummer | 1091182410 |
| Probe | Sekrete |
| Anmeldung | Tierärztliche Gesundheitsdiagnose |
| Empfindlichkeit | 99.80% |
| Spezifität | 97.69% |
| Zertifikat | GMP & ISO9001 & CE |
| Assay Zeit | 10 Minuten |
| OEM&ODM | Verfügbar |
| Haltbarkeitsdauer | 3 Years |
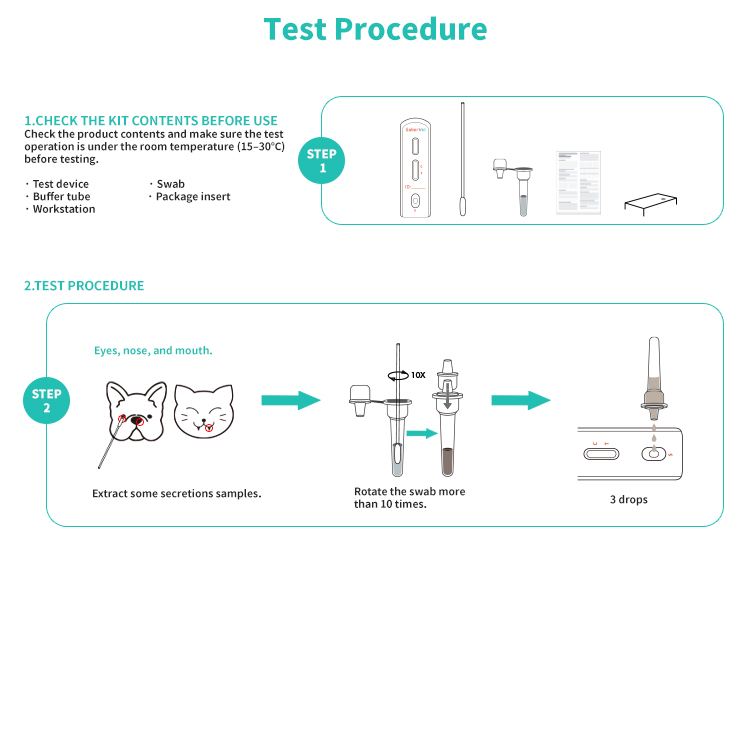
Operation
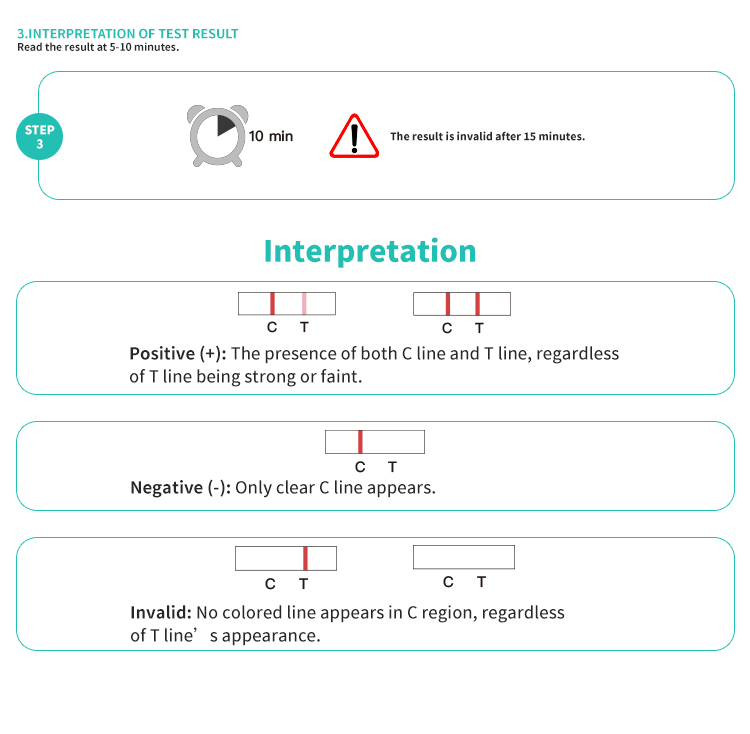
Ergebnisse
Das Tollwutvirus gehört zur Familie der Elastoviridae, der Gattung der Tollwutviren. Die Viruspartikel haben eine elastische Form mit einem Durchmesser von etwa 75 nm und sind als RNA-Virus in einer Kapsel verkapselt. Eine Infektion mit dem Tollwutvirus verursacht Tollwut.
Klinische Symptome der Tollwut
Die Tollwut, auch Hydrophobie genannt, ist eine virulente Zoonose, die durch das Tollwutvirus verursacht wird, das ein breites Spektrum an Infektionen aufweist. Wenn klinische neurologische Anzeichen vorhanden sind, tritt in fast 100% der Fälle der Tod ein.
Dogs with rabies disease will show a more specific expression of terror and squinting, especially when attacked again by external stimuli. In the late stage of rabies, the patient's consciousness gradually disappears, the body will gradually lose weight, will show fear of water, dyspnoea, jaw droop and other characteristics, and there is a wild biting behaviour, and finally will be due to respiratory distress leading to central failure or paralysis and death.
Menschen, die an Tollwut erkrankt sind, zeigen zunächst Manie, Angst vor Wasser, übermäßiges Schwitzen, Tränenfluss, schnellen Pulsschlag, Fieber, erweiterte Pupillen, Atembeschwerden und Verlust der Selbstkontrolle usw., später kommt es zu zentralem Nervenversagen oder Lähmungen, Koma oder Tod.
Transmission of Rabies
Traumatic contact transmission
If scratched or bitten by rabid animals or suspected rabid animals, or contacted with rabies virus-carrying animals and their saliva or blood in the broken skin or mucous membrane, rabies virus can enter into the body through the broken place, and the traumatic contact transmission is the more common way of transmission.
Respiratory transmission
Aerosols of rabies virus may be found in the burrows of rabies virus-carrying animals. If inhaled after entering a burrow, rabies virus can be transmitted through the respiratory tract.
Übertragung über den Verdauungstrakt: Der Verzehr von tollwutinfizierten Lebensmitteln, wie Fleisch und dessen Erzeugnisse von erkrankten Tieren, kann ebenfalls zur Übertragung von Tollwut führen.
Clinical diagnosis of Rabies
Virusisolierung und -kultur: Frisches Hirngewebe wird nach dem Tod von erkrankten Tieren entnommen, und die Gewebeflüssigkeit wird in säugende Mäuse injiziert oder mit zellulärem Gewebe zur Kultur und Amplifikation geimpft, und die Viruspartikel werden mittels Immunfluoreszenztechnik nachgewiesen. Diese Methode eignet sich zur Bestätigung der Diagnose bei toten Tieren, bei denen ein Infektionsverdacht besteht.
Fluoreszenz-Antikörper-Methode: Die Fluoreszenz-Antikörper-Technik (FAT) bezieht sich auf die Färbung von in Aceton fixierten Hirngewebeschnitten mit fluoreszierenden Antikörpern, um das Vorhandensein von viralen Partikeln oder viralen Einschlüssen in Hirngewebeschnitten durch Fluoreszenzmikroskopie zu bestimmen.
Direct Fluorescent Antibody
Direct Fluorescent Antibody (DFA) is the "gold standard" for laboratory diagnosis of rabies and is accredited by the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). The method involves fixing brain tissue slices from suspected diseased animals and binding them with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled monoclonal antibodies to the rabies virus, which can be directly observed by fluorescence microscopy to determine the viral particles.
Rapid immunohistochemistry
Rapid immunohistochemistry (dRIT) is mainly used for the qualitative detection of rabies. The method mainly collects brain tissue samples from suspected diseased animals, and after specific binding with specific rabies virus monoclonal antibody, after staining, the presence of virus particles can be directly observed under the light microscope to determine whether rabies is infected or not.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) makes use of the principle of specific binding of antigen and antibody to determine the negativity and positivity of the pathogen by observing the degree of colour reaction.
Nucleic acid detection technology
Nucleic acid detection of rabies virus usually adopts RT-PCR technology to amplify the target gene fragment, and judgement is made according to the amplification results.
Tollwut-Antikörper-Schnelltest
Antigenne hat einen Tollwut-Antikörper-Schnelltest für Speichel-/Liquorproben entwickelt, der als wirksames Mittel zur Überwachung des Tollwutvirus eingesetzt werden kann.