Description
Intended Use
Newcastle Disease Virus Antigen Rapid Test is a lateral flflow immunoassay intended for the qualitative detection of specifific antigen from Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in laryngeal secretions/cloaca swab sample. The test is useful for determination of NDV infection.
Contents
| Component | 10T/Box |
| Test device | 10 piece |
| Swab | 10 piece |
| Buffer | 10 piece |
Specifications
| Product name | Newcastle Disease Virus Antigen Rapid Test |
| Brand Name | Sabervet |
| Model Number | 1089122420 |
| Specimen | Secretions/Cloaca |
| Application | Vet Health Diagnosis |
| Sensitivity | 99.80% |
| Specificity | 97.69% |
| Certificate | GMP & ISO9001 & CE |
| Assay Time | 10 Minutes |
| OEM&ODM | Available |
| Shelf Life | 3 Years |
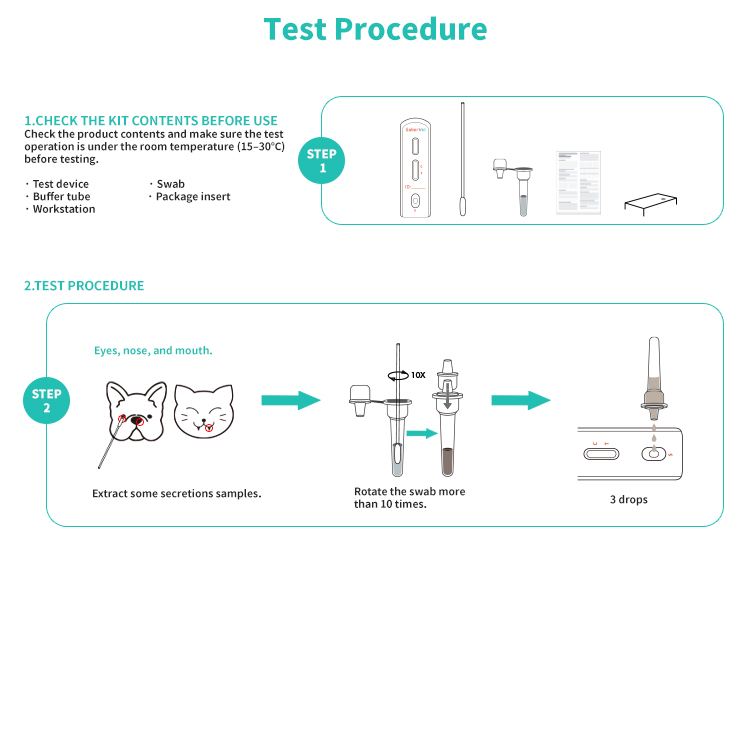
Operation
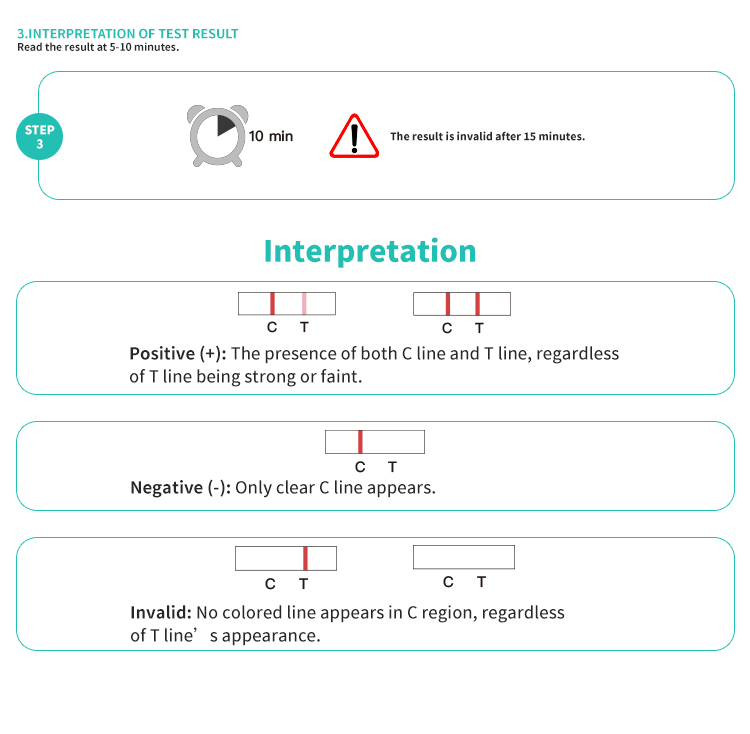
Results
Pathological Introduction
Newcastle disease (ND) is a highly contagious disease of poultry caused by a virulent strain of Newcastle disease virus. It is characterized by high fever, respiratory distress, dysentery, nervous disorders, and hemorrhages of the mucous membranes and plasma membranes.
Since the first outbreak in 1926, Newcastle disease has been reported in more than 100 countries in South America, Asia, Europe, and Africa. The disease has a high morbidity and mortality rate and is a major infectious disease endangering the poultry industry.
Newcastle disease can occur throughout the year, but more in spring and autumn, and there are differences in susceptibility for chickens of different ages, with the highest susceptibility in young and middle chicks. Ducks, geese, other waterfowl, pigeons, turtledoves, crows, sparrows, and other birds can also be infected with the disease.
The main source of infection of Newcastle Disease is sick birds and birds with the virus in the inter-epidemic period, infected chickens the 24 hours before the appearance of clinical symptoms, its mouth, nasal secretions, and feces have virus discharge, the virus can be through the digestive tract, the respiratory tract, but also through the conjunctiva, injured skin and cloacal mucosa invasion of the organism.
The incubation period of Newcastle disease is 21 days. According to the clinical manifestations and the duration of the disease, Newcastle disease is generally divided into the most acute, acute, subacute, or chronic three types.
The most acute type:
Often sudden onset, no characteristic symptoms, and rapid death. Mostly seen in chicks and the early stage of the epidemic.
Acute type:
Exhibits respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and neurological abnormalities. Often begins with respiratory symptoms, followed by dysentery. At first, the body temperature rises to 43~44℃, the appetite decreases or is abolished, and the spirit is depressed. Hens stop laying eggs or soft-shell eggs.
With the development of the disease, more typical symptoms appear. The course of the disease is about 2~5 days. chicks within 1 month of age have a short course of the disease, the symptoms are not obvious, and the mortality rate is high.
Subacute or chronic type:
Initial symptoms are similar to the acute type, soon improved, but at the same time, neurological symptoms, such as wing paralysis, lameness or unsteady standing, head and neck backward or to the side of the twist, often ambidextrous rotating, repeated episodes, and finally can become paralyzed or hemiparalysed, usually after 10~20 days death. It occurs mostly in adult birds in the late epidemic period, with a low case fatality rate.
Means of detection
Laboratory diagnosis: In international trade, there is no designated diagnostic method. An alternative diagnostic method are haemagglutination inhibition test.
Pathogen examination: ① virus culture identification: samples are processed, inoculated with 9-10 day-old SPF chicken embryos, incubated at 37 ℃ for 4 to 7 days, collected urinary allantoic fluid to do HA test to determine the potency, with specific antisera (chicken antisera) or I test to determine the presence of ND virus. ②Virulence assay: intracerebral inoculation pathogenicity index (ICPI) of 1-day-old chicks, intraventricular inoculation pathogenicity index (IVPI) of 6-week-old chicks, and mean time to death (MDT) of chicken embryos.
Serological tests: virus haemagglutination test (HA), virus haemagglutination inhibition test (HI), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA, used for on-site diagnosis, epidemiological investigations, and screening of chicken quarantine at ports of entry and exit).
Sample collection: For virus isolation, brain, lung, spleen, liver, heart, kidney, intestines (including contents), or mouth and nose swabs can be collected from sick, dead, or dying birds, and the above samples can be collected individually or mixed, except for intestinal contents which need to be treated separately.
Or collect tracheal and cloacal swabs from live birds. Swabs collected from chicks or rare birds are prone to damage, and fresh feces can be collected instead. The above samples should be sent to the laboratory immediately for processing or stored at 4°C for testing (not more than 4 days) or at 30°C for testing.
For samples used for serological tests, serum is usually collected.
Treatment options
Diseased quail are of no therapeutic value and cannot be treated and must be culled early. In the early stage of the disease, based on the elimination of sick quails, the other presumed healthy quails immediately with chicken Newcastle disease Ⅳ vaccine for emergency immunization, each quail intramuscular injection of 2 copies.
Normally, we should pay attention to the immunization, and the immunization procedure for Newcastle disease can only be scientifically determined by the HI antibody test.
Generally speaking, the first immunization is carried out at the age of 10 days (Ⅳ series of seedlings dotting the eyes and dropping the nose), and the second immunization (Ⅳ series of seedling drinking water) is carried out after 10-15 days.
In the case of egg partridge or breeder partridge, subcutaneous injection of 0.2 ml of oil emulsion seedling of Newcastle Disease is given 2 weeks before laying of eggs, which can obtain more effective immunity and contain higher maternal antibody, so that the young partridge hatched from this breeder partridge can be passively immunized within 2 weeks.
This disease is an acute infectious disease caused by the Newcastle disease virus, quail and birds can be infected, mostly occurring in the late epidemic in quail. The disease can occur year-round, with a high mortality rate.
Chicken morbidity is mostly acute, subacute, and chronic through, in the clinical treatment of mostly subacute cases, the treatment of commonly used western medicine ribavirin antiviral, Anacin antipyretic antidote, β-lactam antibiotics to prevent secondary infections.
The creation of Itgen not only reinforces the company’s commitment to quality and innovation but also serves as a testament to its unwavering dedication to improving animal health and welfare.Together, we can make a difference. Contact Antigenne now and let’s unlock the future of animal health.