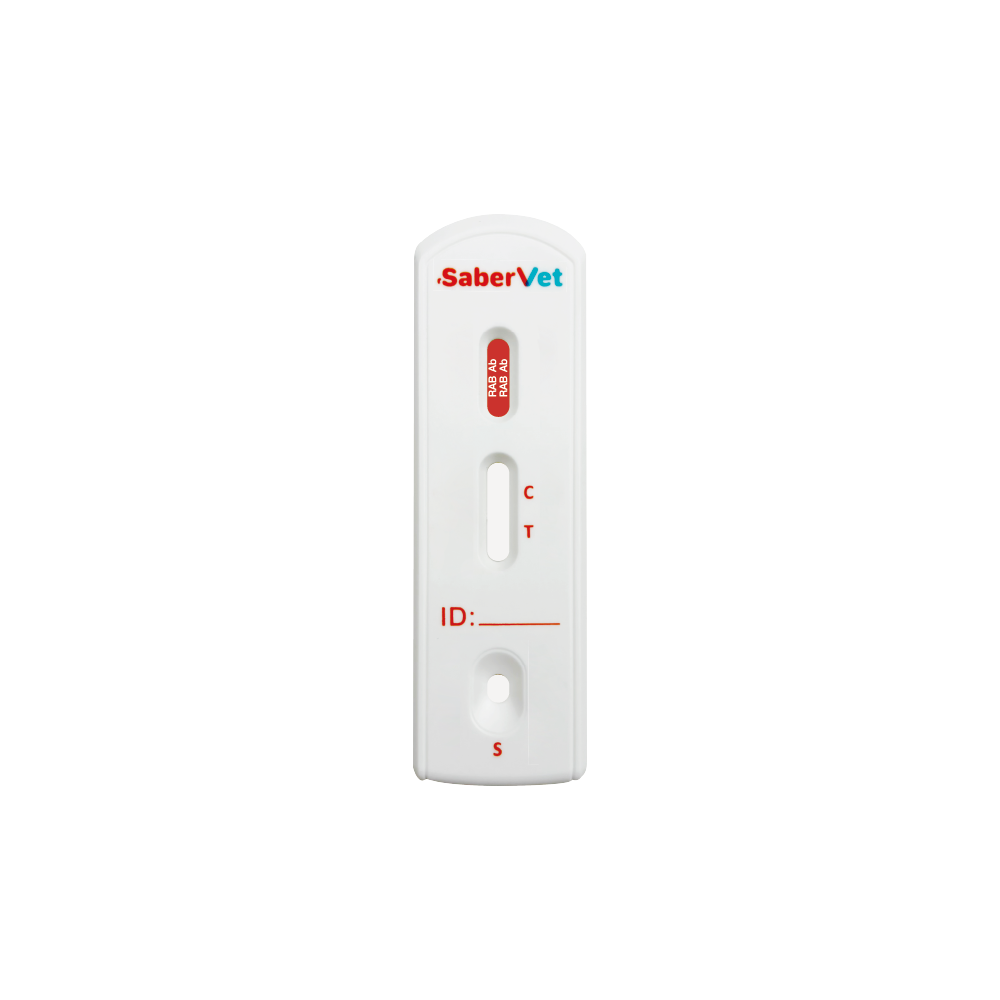
Sabervet Rabies Antibody Rapid Test
SaberVet Rabies Antibody Rapid Test offered by Antigenne is a lateral flow immunoassay intended for the qualitative detection of Rabies Antibody (RAB Ab) in serum/plasma sample.
Technical Specifications
Detailed technical parameters and product description for professional evaluation.
Quality Standards & Certifications
ITGen maintains the highest quality standards with comprehensive certifications and batch consistency guarantees.
Certifications & Standards
Quality Guarantees
Batch Consistency
Every batch tested for consistent performance
Quality Control
Rigorous QC testing at every production stage
Traceability
Complete batch tracking and documentation
Custom Solutions & Bulk Sourcing
Comprehensive OEM/ODM services with flexible bulk pricing and global logistics support for business partners.
OEM/ODM Services
- Custom Brand Packaging
- Private Label Solutions
- Product Customization
- Design Modifications
Bulk Pricing
- Volume Discounts
- Tiered Pricing Structure
- Long-term Contracts
- Flexible Payment Terms
Global Logistics
- Worldwide Shipping
- Fast Delivery Options
- Cold Chain Logistics
- Documentation Support
Partnership Benefits
48-Hour Quote Response
Fast turnaround time for all inquiries and custom requirements.
24/7 Technical Support
Comprehensive technical assistance and product training.
Quality Assurance
ISO GMP certified manufacturing with consistent quality control.
Get Custom Quote
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about product usage, storage, and bulk ordering.
How accurate are the test results?
Our rapid test kits demonstrate 99% sensitivity and 98.8% specificity in clinical trials, ensuring highly accurate diagnostic results for veterinary professionals.
What is the shelf life and storage requirement?
The product has a 24-month shelf life when stored at 2-30°C. Room temperature storage makes it convenient for field use without refrigeration requirements.
What are the minimum order quantities for bulk purchases?
Minimum order quantities vary by product and customization requirements. Contact our sales team for specific MOQ information and volume pricing tiers.
Do you provide OEM/ODM services?
Yes, we offer comprehensive OEM/ODM services including custom packaging, private labeling, and product modifications to meet specific market requirements.
What shipping options are available for international orders?
We provide worldwide shipping with express delivery options. Our logistics team handles all documentation and ensures proper cold chain management when required.